Understanding the Importance of Retractor Medical Instruments in Modern Medicine
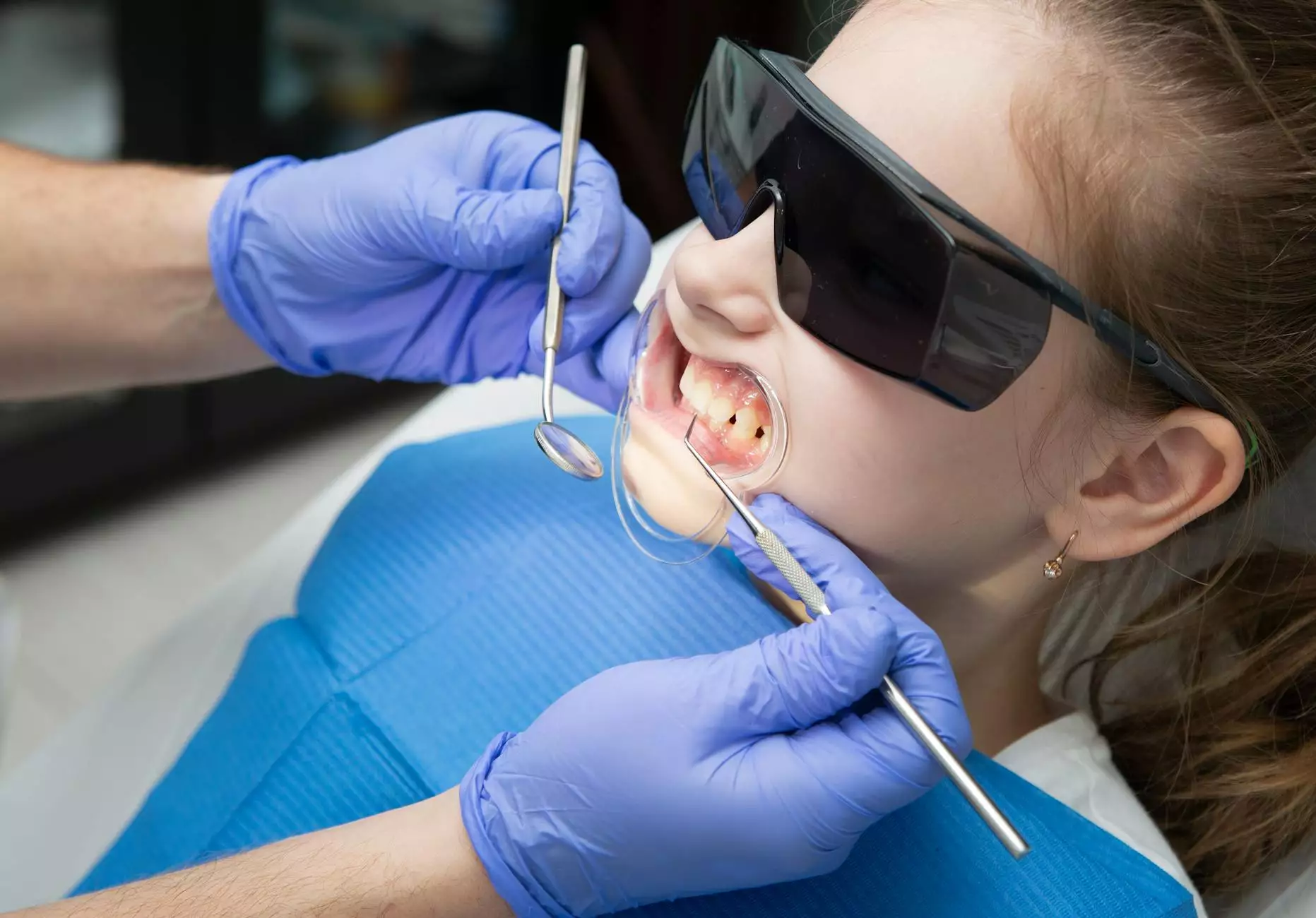
In the realm of modern medicine, precision and efficiency are crucial for successful surgical outcomes. One key instrument that plays a pivotal role in various surgical procedures is the retractor medical instrument. These instruments serve to hold back tissues and organs, allowing surgeons clear access to the areas they need to work on. In this article, we will delve deep into the world of retractors, exploring their history, types, uses, and why they are indispensable in surgical settings.
The Historical Evolution of Retractor Medical Instruments
Retractors have a long-standing place in surgical history that dates back to ancient civilizations. Initially, tools resembling modern retractors were made from rudimentary materials like metal and wood. Over centuries, the design and functionality of these instruments have vastly improved, leading to the sophisticated retractors we see today.
- Ancient Egypt: Some of the earliest surgical tools were discovered in Egyptian tombs, which included metal instruments that resemble modern-day retractors.
- Greece and Rome: Ancient physicians utilized various tools, some of which were designed specifically to hold incisions open during surgery.
- Renaissance Period: This era marked significant advancements in surgical techniques and tools, leading to the development of more refined retractors.
What Are Retractor Medical Instruments?
Retractor medical instruments are devices designed to maintain the position of tissues during surgical procedures. By holding back skin, muscle, and organs, retractors provide surgeons with improved visibility and access to the surgical site, which can be critical for successful outcomes.
Types of Retractor Medical Instruments
There are several types of retractors, each designed for specific procedures and applications. Understanding these types is essential for proper usage and efficiency in the operating room.
1. Hand-held Retractors
Hand-held retractors are manually operated tools that require assistance from another surgical team member to hold them in place, enabling surgeons to focus on the procedure. Examples include:
- Adson Retractor: A thin, flat retractor with angled ends ideal for small incisions.
- Deaver Retractor: Known for its wide blade, useful in deep abdominal or thoracic surgeries.
2. Self-retaining Retractors
These retractors are designed to hold themselves in place, freeing up the surgeon's hands. They are particularly useful for longer procedures. Notable examples include:
- Bookwalter Retractor: A versatile retractor that can be adjusted for various angles and depths.
- Richards Retractor: Features various attachments that enable multiple retraction options.
3. Speculum Retractors
These are specialized retractors primarily used in gynecological and rectal examinations. Their design allows for maximum visualization of the internal structures.
Materials Used in Retractor Medical Instruments
Advancements in material science have led to the production of retractors that are not only effective but also safe for patients. Common materials used include:
- Stainless Steel: The most common material due to its durability, resistance to rust, and ability to be sterilized.
- Plastic: Some retractors are made from high-grade plastics, offering a lightweight alternative for certain applications.
- Titanium: Known for its strength and light weight, titanium retractors are becoming increasingly popular.
How Retractor Medical Instruments Enhance Surgical Procedures
The importance of retractor medical instruments in surgery cannot be overstated. They offer numerous benefits that significantly enhance the surgical experience for both the surgeon and the patient.
Improved Visibility
One of the primary advantages of using retractors is the improved visibility they provide. By holding tissues aside, retractors allow the surgeon to see the surgical site clearly, which is crucial for:
- Precise Cuts: Minimizing the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
- Accurate Suture Placement: Ensuring that incisions are properly closed.
Reduced Procedure Time
Retractors help reduce the time spent in the operating room by:
- Streamlining Workflow: Freeing up the surgeon's hands enables continuous focus on the task at hand.
- Minimizing distractions: With clear access to the area of interest, the surgical team can work more efficiently.
Enhanced Patient Safety
By allowing for more precise operations and reducing the risk of complications, retractors contribute to an overall increase in patient safety. This is particularly notable in:
- Minimally Invasive Procedures: Where prolonged exposure could lead to infection or other complications.
- Complex Surgeries: Where multiple layers of tissue require careful handling.
Best Practices for Using Retractor Medical Instruments
To leverage the full potential of retractor medical instruments, surgical teams must adhere to best practices regarding their use, maintenance, and sterilization:
Selection of the Appropriate Retractor
Choosing the right type of retractor is essential depending on the surgical procedure. Factors to consider include:
- Type of Surgery: Different surgeries will require different retractors.
- Size of the Incision: Larger incisions may need more robust retractors.
Proper Handling Techniques
Surgeons and assistants should be trained in handling retractors to ensure they are used effectively and safely. This includes:
- Firm Grip: Ensuring the retractor remains in place without slipping.
- Gentle Pressure: Avoiding excessive force that could damage tissues.
Regular Maintenance and Sterilization
To prevent infection and ensure longevity, retractors should be properly maintained. This involves:
- Thorough Cleaning: Using appropriate cleaning solutions to remove blood and tissue residue.
- Periodic Inspections: Checking for any defects or damage that could compromise the instrument.
The Future of Retractor Medical Instruments
The future of surgical instruments, including retractors, is poised for exciting advancements. Innovations driven by technology aim to improve usability, safety, and effectiveness. Emerging trends include:
- Smart Retractors: Instruments with built-in sensors that can provide real-time feedback to surgeons about tissue conditions.
- 3D Printing: Enabling customized retractors tailored to individual surgical needs.
- Enhanced Materials: Innovations in biocompatible materials may lead to retractors with improved safety profiles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, retractor medical instruments are fundamental tools in the modern surgical arena. Their evolution reflects the advancements in medicine and technology, providing critical support to surgeons around the world. As we look to the future, continued innovation promises to enhance their effectiveness, safety, and usability, ultimately benefiting patient care.
For further information about the best retractor medical instruments and other medical supplies, visit new-medinstruments.com.









