The Essential Role of **Oncology Doctors** in Modern Medicine

Understanding Oncology
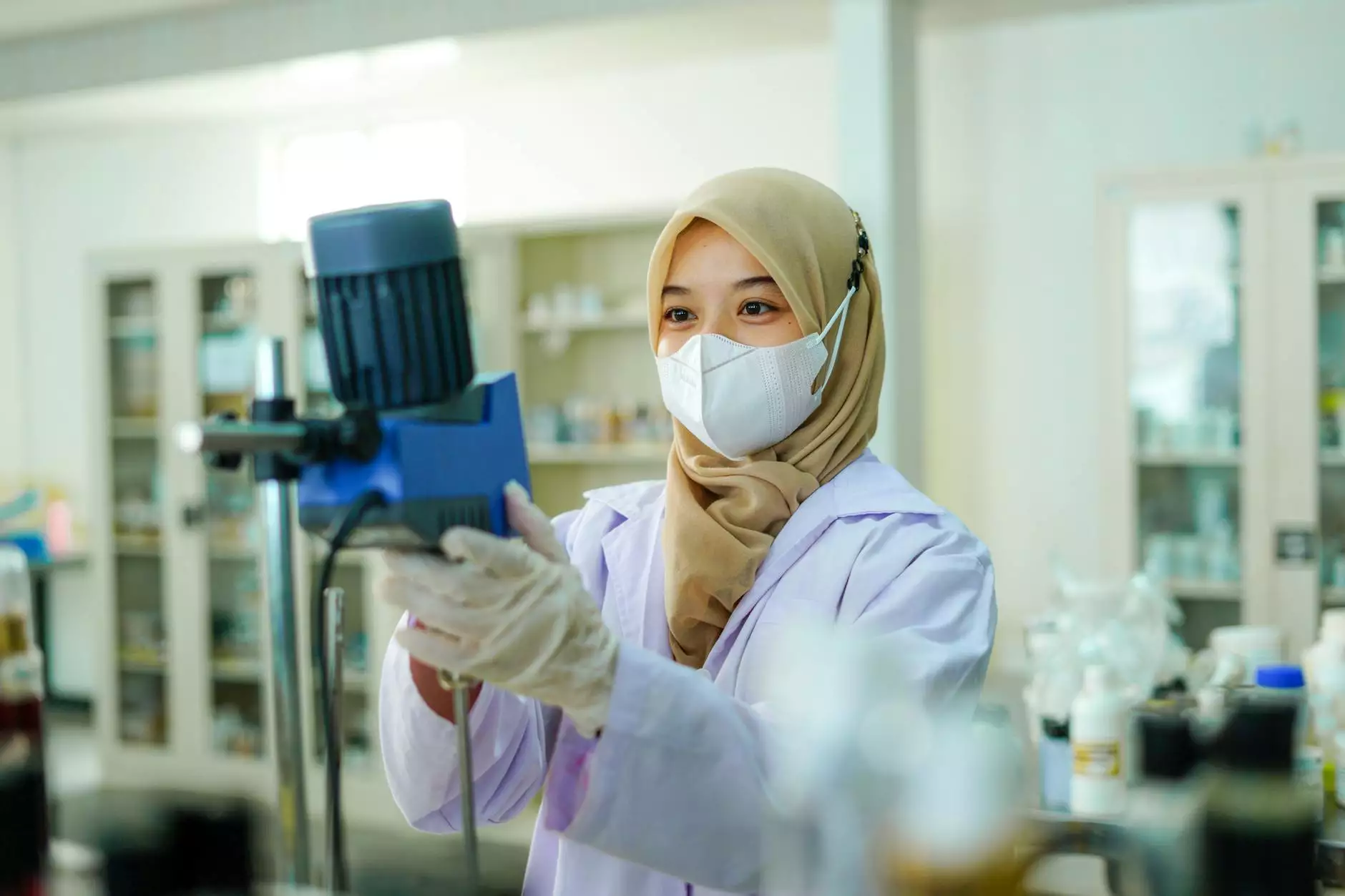
Oncology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the diagnosis, treatment, and management of cancer. As cancer remains one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality worldwide, the contributions of oncology doctors are increasingly vital. These specialists dedicate their careers to understanding the complex biological behaviors of tumors and providing patients with effective treatment plans.
The Journey to Becoming an Oncology Doctor
The path to becoming an oncology doctor is rigorous and demanding. It typically involves:
- A bachelor's degree - usually in a science-related field.
- Medical school - where candidates earn their Doctor of Medicine (MD) or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO) degree.
- Residency program - a 3- to 7-year program focused on internal medicine or pediatrics, where future oncology doctors begin their specialized training.
- Fellowship in oncology - an additional 2-4 years of training in oncology, where they gain hands-on experience in diagnosing and treating various types of cancer.
Types of Oncology Doctors
There are several sub-specialties within oncology, allowing oncology doctors to focus on particular aspects of cancer treatment:
- Medical Oncologists - specialists in the treatment of cancer using chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and targeted therapy.
- Radiation Oncologists - focus on treating cancer using radiation therapy.
- Surgical Oncologists - perform surgeries to remove tumors and surrounding tissue.
- Pediatric Oncologists - specialize in diagnosing and treating cancers in children.
The Role of An Oncology Doctor
Oncology doctors take on multiple roles in patient care and management:
- Diagnosis - They conduct thorough evaluations, including physical examinations, laboratory tests, imaging tests, and biopsies.
- Creating Treatment Plans - Based on the type and stage of cancer, they develop personalized treatment plans that may include chemotherapy, radiation, surgery, or a combination of these modalities.
- Ongoing Management - Oncology doctors monitor the patient's progress and make necessary adjustments to therapy, addressing any side effects or complications.
- Consultation - They collaborate with other specialists, including pharmacists, radiologists, and pathologists, to provide holistic care.
- Patient Education - Providing information about cancer, treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes for better outcomes.
Technological Advances in Oncology
The field of oncology is rapidly evolving due to advancements in technology. Oncology doctors are now utilizing pioneering techniques and tools to improve patient care, including:
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing allows oncology doctors to understand the genetic makeup of a patient's tumor, enabling them to choose targeted therapies that are more effective and with fewer side effects.
Immunotherapy
This innovative approach harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Oncology doctors are at the forefront of administering immunotherapy, which has revolutionized treatment for certain types of cancers.
Precision Medicine
Precision medicine tailors treatment based on individual patient characteristics, including their genetics and the specific features of their cancer. This personalized approach is becoming a standard practice in oncology.
Telemedicine
In recent years, telemedicine has changed the way oncology doctors interact with patients. Virtual consultations have improved accessibility for patients, particularly those in remote areas.
The Importance of Rehabilitation and Support
The journey through cancer treatment can be challenging and exhausting. Oncology doctors play a crucial role in ensuring that patients receive not only medical treatment but also supportive care. This includes:
Psychosocial Support
Cancer impacts mental health significantly. Oncology doctors often collaborate with psychologists and counselors to provide comprehensive care, addressing emotional and psychological needs.
Palliative Care
Palliative care focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses. It can be integrated at any stage of treatment, and oncology doctors advocate for palliative measures to manage pain and other distressing symptoms.
Rehabilitation Programs
Many patients may benefit from rehabilitation services, including physical, occupational, and nutritional therapy. Oncology doctors work with a multidisciplinary team to design optimal recovery plans.
Challenges Faced by Oncology Doctors
Despite the rewarding nature of their work, oncology doctors face several challenges:
Keeping Up With Rapid Developments
The field of oncology is constantly evolving, and staying updated with the latest research, clinical trials, and treatment modalities can be overwhelming.
Emotional Burden
Given the gravity of cancer diagnoses and the emotional strain that accompanies treatment discussions, oncology doctors must navigate complex emotional landscapes, both for themselves and their patients.
Healthcare Accessibility
Ensuring that all patients have access to quality oncology care is a critical issue. Oncology doctors often advocate for healthcare policies that improve patient access to essential treatments.
The Future of Oncology
The horizon for the field of oncology is bright, with newcomers consistently pushing the boundaries of what's possible in cancer treatment. Oncology doctors are excited about:
Increased Focus on Preventive Oncology
Emphasizing prevention through lifestyle changes and vaccinations can drastically reduce cancer incidence. Oncology doctors advocate for educational programs to raise awareness about cancer prevention methods.
Advancements in Research
Ongoing clinical trials are crucial for developing new treatments. Oncology doctors encourage patients to consider participating in trials that may contribute to broader scientific knowledge and potentially offer cutting-edge treatments.
Collaborative Care Models
The future lies in collaborative care where oncology doctors work alongside other medical professionals to provide comprehensive treatment plans, considering every aspect of a patient's health and wellbeing.
Conclusion
Oncology doctors are pivotal in the fight against cancer. Their expertise, compassion, and dedication serve as a beacon of hope for patients navigating one of life’s most challenging journeys. With ever-evolving knowledge and treatment modalities, oncology doctors remain committed to providing the highest level of care, improving patient outcomes, and enriching the quality of life for cancer patients everywhere.
As we look toward the future, the profession will continue to adapt and embrace new technologies and methodologies, ensuring that the battle against cancer is fought with the best possible resources and understanding.